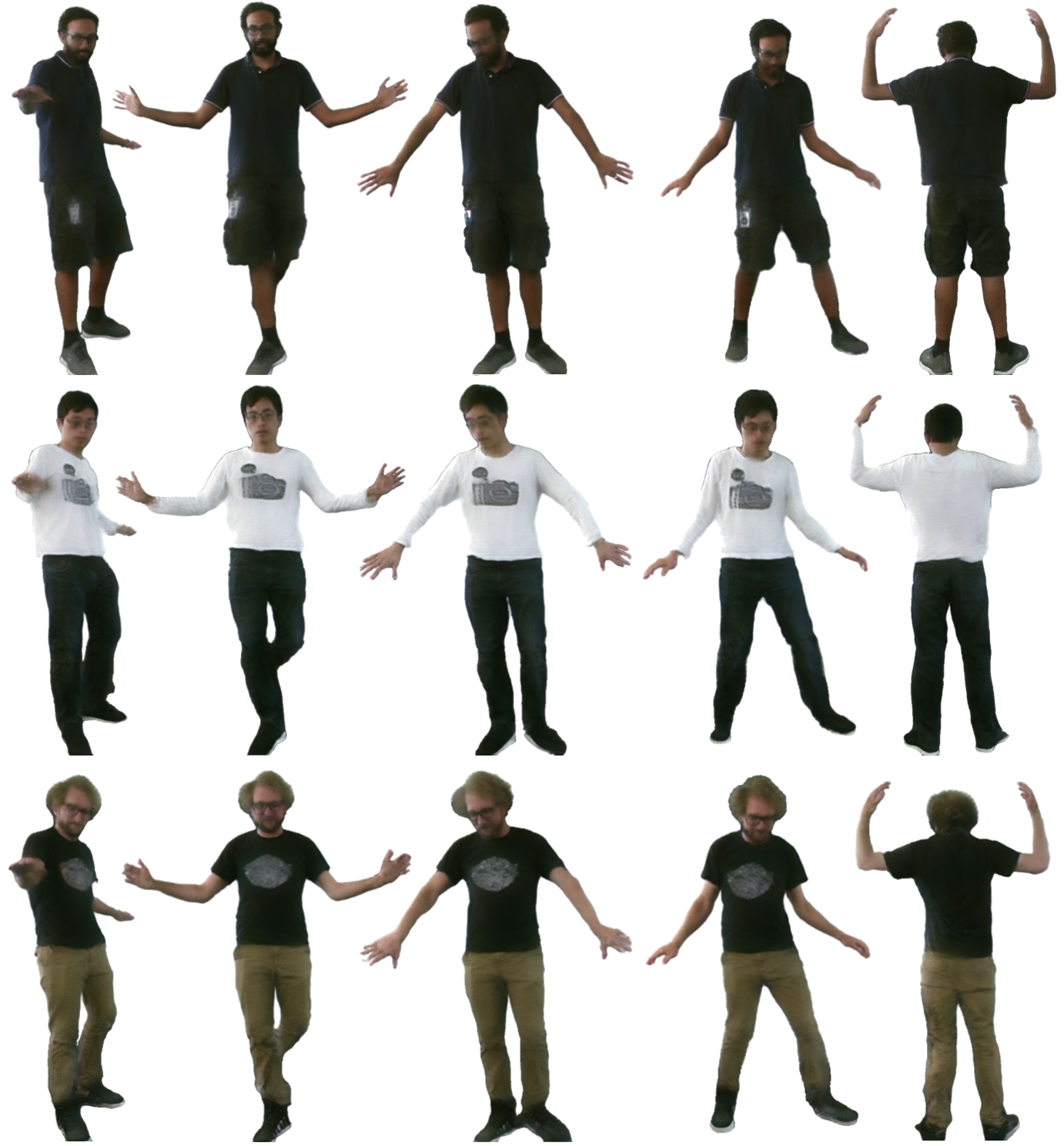|
The combination of traditional rendering with neural
networks in Deferred Neural Rendering (DNR) provides a compelling balance between computational complexity and realism of the resulting images. Using skinned
meshes for rendering articulating objects is a natural extension for the DNR framework and would open it up to a
plethora of applications. However, in this case the neural
shading step must account for deformations that are possibly not captured in the mesh, as well as alignment inaccuracies and dynamics—which can confound the DNR
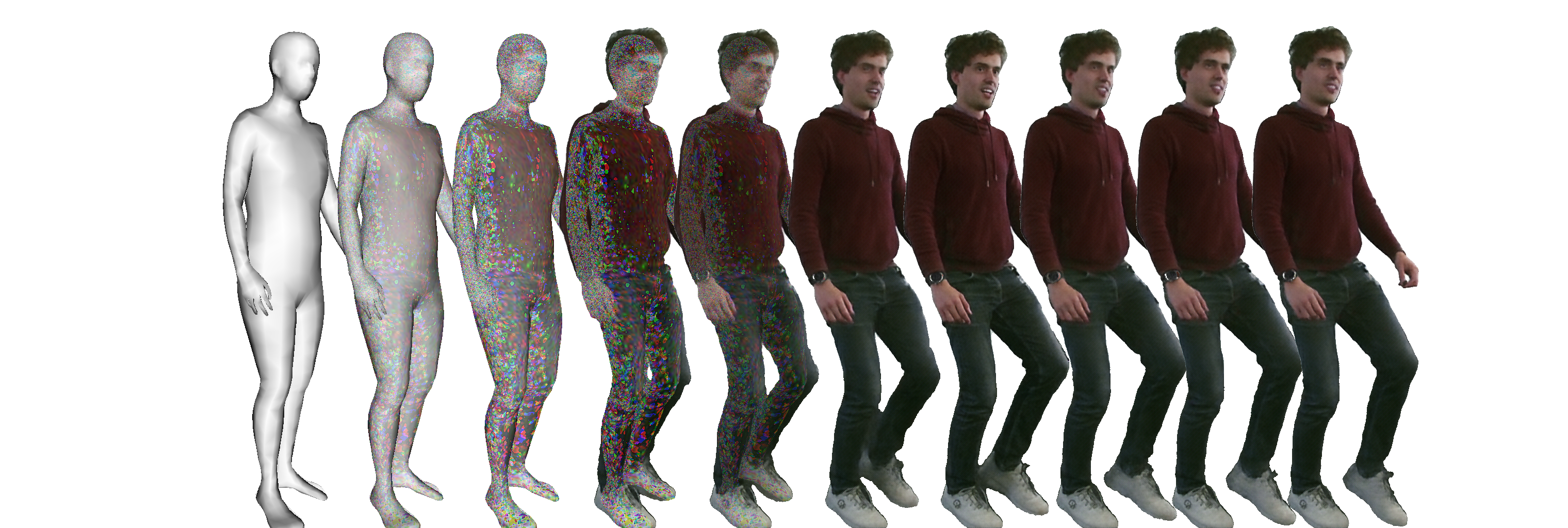
pipeline. We present Articulated Neural Rendering (ANR), a
novel framework based on DNR which explicitly addresses
its limitations for virtual human avatars. We show the superiority of ANR not only with respect to DNR but also
with methods specialized for avatar creation and animation. In two user studies, we observe a clear preference
for our avatar model and we demonstrate state-of-the-art
performance on quantitative evaluation metrics. Perceptually, we observe better temporal stability, level of detail and
plausibility.
|